Connecting Rod
|
1. |
Check the side clearance between piston and connecting rod.
Using filler gauge, measure the side clearance while moving the
connecting rod back and forth.
Side clearance
Standard : 0.1 ~ 0.25 mm (0.0039 ~ 0.0098 in)
Maximum : 0.35 mm (0.0138 in)
|
| A. |
If out-of-tolerance, install a new connecting rod.
|
| B. |
If still out-of-tolerance after connecting rod replacement,
replace the crankshaft.
|
|
|
2. |
Check the connecting rod bearing oil clearance.
|
(1) |
Check the match marks on the connecting rod and cap are
aligned to ensure correct reassembly.
|
|
(2) |
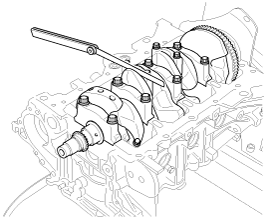
Remove the 2 connecting rod cap bolts.
|
|
(3) |
Remove the connecting rod cap and lower bearing.
|
|
(4) |
Clean the crankshaft pin journal and bearing.
|
|
(5) |
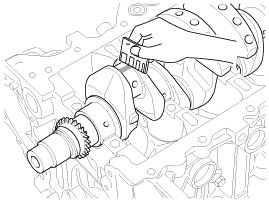
Place a plastigage across the crankshaft pin journal.
|
|
(6) |
Reinstall the lower bearing and cap, and tighten the bolts.
Tightening torque :
17.7 ~ 21.6 N.m (1.8 ~ 2.2 kgf.m, 13.0 ~ 15.9
lb-ft) + 88°~92°
|
|
• |
Do not turn the crankshaft.
|
|
• |
Always use new connecting rod cap bolts.
Connecting rod cap bolts are toque-to-yield
bolts designed to be permanently elongated beyond
the state of elasticity when torqued, so if
the bolts are removed and reused, it may cause
the bolts to break or fail to maintain clamping
force.
|
|
|
|
(7) |
Remove the connecting rod cap and lower bearing.
|
|
(8) |
Measure the plastigage at its widest point.
Bearing oil clearance
:
0.032 ~ 0.052 mm (0.0013 ~ 0.0020 in)
|
|
|
(9) |
If the measurement from the plastigage is too wide or
too narrow, remove the upper and lower bearing and then install
a new bearings with the same color mark.
Recheck the oil clearance.
|
Do not file, shim on scrape the bearings or the
caps to adjust clearance.
|
|
|
(10) |
If the plastigage shows the clearance is still incorrect,
try the next larger or smaller bearing. Recheck the oil clearance.
|
If the proper clearance cannot be obtained by
using the appropriate larger or smaller bearings, replace
the crankshaft and start over.
|
|
If the marks are indecipherable because of an
accumulation of dirt and dust, do not scrub them with
a wire brush or scraper. Clean them only with solvent
or detergent.
|
|
|
(11) |
Select the bearing by using the selection table.
Connecting Rod Bearing Selection Table
Connecting rod bearing
|
Connecting rod mark
|
A, 0
|
B, 00
|
C, 000
|
Crank shaft pin journal
mark
|
1
|
E (Red)
|
D (Green)
|
C (None)
|
2
|
D (Green)
|
C (None)
|
B (Black)
|
3
|
C (None)
|
B (Black)
|
A (Blue)
|
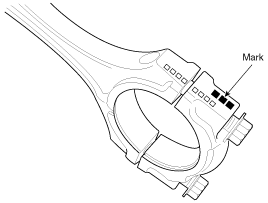
Discrimination Of Connecting Rod
Mark
|
Connecting rod big-end
inner diameter
|
A, 0
|
45.000 ~ 45.006 mm
(1.7717 ~ 1.7719 in)
|
B, 00
|
45.006 ~ 45.012 mm
(1.7719 ~ 1.7721 in)
|
C, 000
|
45.012 ~ 45.018 mm
(1.7721 ~ 1.7724 in)
|
Discrimination Of Crankshaft Pin Journal
Mark
|
Crankshaft pin journal
outer diameter
|
1
|
41.966 ~ 41.972 mm
(1.6522 ~ 1.6524 in)
|
2
|
41.960 ~ 41.966 mm
(1.6520 ~ 1.6522 in)
|
3
|
41.954 ~ 41.960 mm
(1.6517 ~ 1.6520 in)
|
[Type A]
Top surface stamp
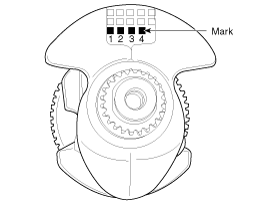
[Type B]
Bottom surface stamp
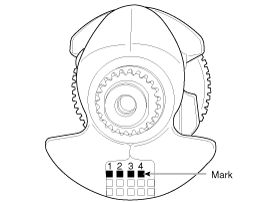
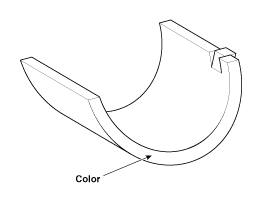
Discrimination Of Connecting Rod Bearing
Class
|
Color
|
Connecting rod bearing
thickness
|
A
|
Blue
|
1.514 ~ 1.517 mm
(0.0596 ~ 0.0597 in)
|
B
|
Black
|
1.511 ~ 1.514 mm
(0.0595 ~ 0.0596 in)
|
C
|
None
|
1.508 ~ 1.511 mm
(0.0594 ~ 0.0595 in)
|
D
|
Green
|
1.505 ~ 1.508 mm
(0.0593 ~ 0.0594 in)
|
E
|
Red or Yellow
|
1.502 ~ 1.505 mm
(0.0591 ~ 0.0593 in)
|
|
|
|
3. |
Check the connecting rods.
|
(1) |
When reinstalling, make sure that cylinder numbers put
on the connecting rod and cap at disassembly match. When a new
connecting rod is installed, make sure that the notches for
holding the bearing in place are on the same side.
|
|
(2) |
Replace the connecting rod if it is damaged on the thrust
faces at either end. Also if step wear or a severely rough surface
of the inside diameter of the small end is apparent, the rod
must be replaced as well.
|
|
(3) |
Using a connecting rod aligning tool, check the rod for
bend and twist. If the measured value is close to the repair
limit, correct the rod by a press. Any connecting rod that has
been severely bent or distorted should be replaced.
Allowable bend of connecting
rod :
0.05 mm (0.0020 in) or less / 100 mm (3.94 in)
Allowable twist of connecting
rod :
0.1 mm (0.0039 in ) or less / 100 mm (3.94 in)
|
|
|
Piston
|
1. |
Clean the piston.
|
(1) |
Using a gasket scraper, remove the carbon from the piston
top.
|
|
(2) |
Using a groove cleaning tool or broken ring, clean the
piston ring grooves.
|
|
(3) |
Using solvent and a brush, thoroughly clean the piston.
|
|
|
2. |
Check the piston-to-cylinder clearance by calculating the difference
between the cylinder bore inner diameter and the piston outer diameter.
Piston-to-cylinder clearance
:
0.02 ~ 0.04 mm (0.0008 ~ 0.0016 in)
|
|
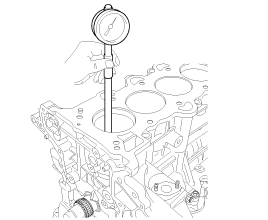
(1) |
Using a cylinder bore gauge, measure the cylinder bore
diameter at position in the thrust and axial direction.
Cylinder bore diameter
:
77.00 ~ 77.03 mm (3.0315 ~ 3.0327 in)
|
|
|
(2) |
Measure the piston outside diameter at 33.9 mm (1.5697
in) from top land of the piston.
Piston outside diameter
:
76.97 ~ 77.00 mm (3.0303 ~ 3.0315 in)
|
|
|
|
3. |
Select the piston matching with cylinder bore class.
Piston-to-cylinder clearance
:
0.02 ~ 0.04 mm (0.0008 ~ 0.0016 in)
|
|
(1) |
Check the cylinder bore size mark on the side of the cylinder
block.
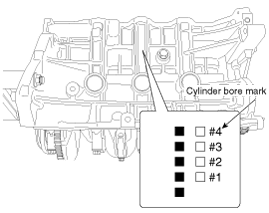
Discrimination Of Cylinder Bore
Mark
|
Cylinder bore inner
diameter
|
A
|
77.00 ~ 77.01 mm
(3.0315 ~ 3.0319 in)
|
B
|
77.01 ~ 77.02 mm
(3.0319 ~ 3.0323 in)
|
C
|
77.02 ~ 77.03 mm
(3.0323 ~ 3.0327 in)
|
|
|
(2) |
Check the piston size mark on the piston top face.
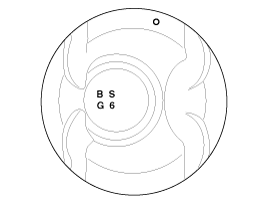
A : Grade
S : ISG type
G : Gasoline engine
6 : 1.6L
Discrimination Of Piston Outer Diameter
Mark
|
Piston outer diameter
|
A
|
76.97 ~ 76.98 mm
(3.0303 ~ 3.0307 in)
|
B
|
76.98 ~ 76.99 mm
(3.0307 ~ 3.0311 in)
|
C
|
76.99 ~ 77.00 mm
(3.0311 ~ 3.0315 in)
|
|
|
Piston Rings
|
1. |
Inspect the piston ring side clearance.
Using a feeler gauge, measure the clearance between new piston
ring and the wall of ring groove.
Piston ring side clearance
[Standard]
No.1 ring : 0.04 ~ 0.08 mm (0.0015 ~ 0.0031 in)
No.2 ring : 0.04 ~ 0.08 mm (0.0015 ~ 0.0031 in)
Oil ring : 0.06 ~ 0.135 mm (0.0024 ~ 0.0053 in)
[Limit]
No.1 ring : 0.1 mm (0.0039 in)
No.2 ring : 0.1 mm ( 0.0039 in)
Oil ring : 0.2 mm ( 0.0079 in)
|
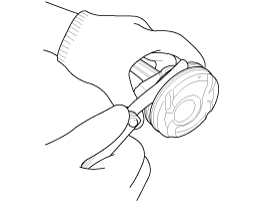
If the clearance is greater than maximum, replace the piston.
|
|
2. |
Inspect the piston ring end gap.
To measure the piston ring end gap, insert a piston ring into
the cylinder bore. Position the ring at right angles to the cylinder
wall by gently pressing it down with a piston. Measure the gap with
a feeler gauge.
Piston ring end gap
[Standard]
No.1 ring : 0.14 ~ 0.28 mm (0.0079 ~ 0.0138 in)
No.2 ring : 0.30 ~ 0.45 mm (0.0118 ~ 0.0177 in)
Oil ring : 0.20 ~ 0.50 mm (0.0079 ~ 0.0276 in)
[Limit]
No.1 ring : 0.3 mm (0.0118 in)
No.2 ring : 0.5 mm (0.0197 in)
Oil ring : 0.8 mm (0.0315 in)
|
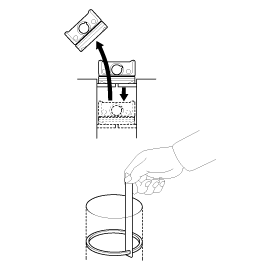
If the gap exceeds the specifications, replace the piston rings.
If the gap is too large, recheck the cylinder bore inner diameter. If
the bore is over the specifications, the cylinder block must be rebored.
|
Piston Pins
|
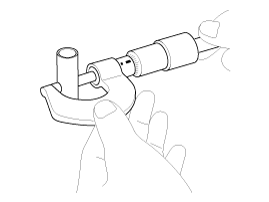
1. |
Measure the outer diameter of piston pin
Piston pin diameter :
18.001 ~ 18.006 mm (0.7087 ~ 0.7089 in)
|
|
|
2. |
Measure the piston pin-to-piston clearance.
Piston pin-to-piston clearance
:
0.010 ~ 0.020 mm (0.0004 ~ 0.0008 in)
|
|
|
3. |
Check the difference between the piston pin outer diameter and
the connecting rod small end inner diameter.
Piston pin-to-connecting rod
interference :
-0.032 ~ -0.016 mm (-0.0013 ~ -0.0006 in)
|
|
•
Use fender covers to avoid damaging painted surfaces.
•
...
•
Thoroughly clean all parts to assembled.
•
...
See also:
Installation
1.
Install in the reverse order of removal.
...
Vehicle weight
This section will guide you in the proper loading of your vehicle and/or trailer,
to keep your loaded vehicle weight within its design rating capability, with or
without a trailer. Properly loadin ...
Front seat adjustment - power (if equipped)
The front seat can be adjusted by using the control switches located on the outside
of the seat cushion.
Before driving, adjust the seat to the proper position so you can easily control
the steer ...
 Kia Soul: Piston and Connecting Rod Inspection
Kia Soul: Piston and Connecting Rod Inspection Piston and Connecting Rod Disassembly
Piston and Connecting Rod Disassembly Piston and Connecting Rod Reassembly
Piston and Connecting Rod Reassembly












